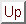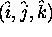 coordinate system.
The direction of
coordinate system.
The direction of 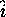 is parallel to the center azimuth angle
of the CAPPI scan.
is parallel to the center azimuth angle
of the CAPPI scan.

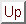


CAPPI scans are formed from boundary layer volume scans of the VIL.
Figure 24 illustrates a lidar backscatter profile
in a lidar-centered cartesian 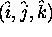 coordinate system.
The direction of
coordinate system.
The direction of 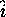 is parallel to the center azimuth angle
of the CAPPI scan.
is parallel to the center azimuth angle
of the CAPPI scan.
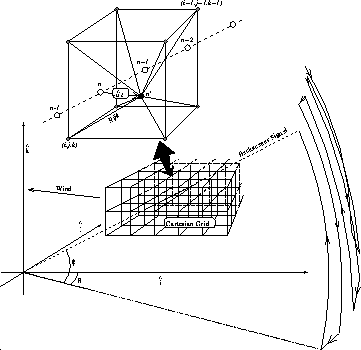
Figure 24: The backscatter signal geometry in cartesian coordinates.
The lidar is located at the origin of 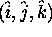 coordinate system.
Sample point n is
moved upwind to correct a distortion due to wind during scanning.
Line Rijk is the distance from the corrected sample point
coordinate system.
Sample point n is
moved upwind to correct a distortion due to wind during scanning.
Line Rijk is the distance from the corrected sample point 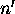 to
grid point
to
grid point 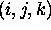 .
.
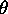 is the azimuth scan angle;
is the azimuth scan angle; 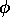 is the elevation scan angle.
is the elevation scan angle.
Since wind moves aerosol structures during scanning,
each backscatter signal location is corrected
by moving it a distance 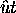 upwind, where
upwind, where
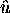 is the mean wind vector and t is the time elapsed
from the first sample in the volume scan.
A priori mean wind information for the correction is not required,
since the analysis can be repeated using the result from the previous
analysis loop as the mean wind estimate
is the mean wind vector and t is the time elapsed
from the first sample in the volume scan.
A priori mean wind information for the correction is not required,
since the analysis can be repeated using the result from the previous
analysis loop as the mean wind estimate 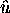 .
Usually, when no correction for the wind (i.e. zero wind speed) is
performed in the first iteration, no more than one iteration
of the wind analysis loop is required [43].
After the correction, the signal amplitude
.
Usually, when no correction for the wind (i.e. zero wind speed) is
performed in the first iteration, no more than one iteration
of the wind analysis loop is required [43].
After the correction, the signal amplitude 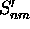 of each data point is averaged to
the eight closest grid points with weights as defined by the following
of each data point is averaged to
the eight closest grid points with weights as defined by the following
where Rijk is the distance between the
corrected signal point 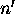 and the grid point
and the grid point 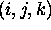 .
.
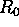 is the distance between the opposite corner points
is the distance between the opposite corner points
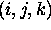 and
and 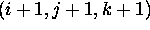 .
The signal intensity in each point
.
The signal intensity in each point 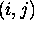 in a CAPPI scan at altitude level
k is expressed as
in a CAPPI scan at altitude level
k is expressed as
When using a dense grid spacing, some grid cells at
long ranges remain unsampled.
These holes are filled by linearly interpolating the closest sampled cells
as follows.
First, single, empty pixels are filled by the average of their neighboring
sampled pixels.
Then, empty lines in 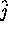 -direction are linearly interpolated
between the sampled border pixels, unless the length of
the empty line exceeds 150 m.
Finally, empty lines in
-direction are linearly interpolated
between the sampled border pixels, unless the length of
the empty line exceeds 150 m.
Finally, empty lines in 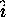 -direction are interpolated similarly.
Several other interpolation schemes were also studied, but
the one above proved to be fast and
preserved the coherence between subsequent CAPPI planes.
If sparser grid spacing was used to avoid empty pixels,
the spatial resolution would be reduced at the closer range
where the quality of the signal is best.
-direction are interpolated similarly.
Several other interpolation schemes were also studied, but
the one above proved to be fast and
preserved the coherence between subsequent CAPPI planes.
If sparser grid spacing was used to avoid empty pixels,
the spatial resolution would be reduced at the closer range
where the quality of the signal is best.